ListView
A scrollable list of controls arranged linearly.
ListView is the most commonly used scrolling control. It displays its children one after another in the scroll direction. In the cross axis, the children are required to fill the ListView.
Inherits: LayoutControl, ScrollableControl, AdaptiveControl
Properties
-
build_controls_on_demand(bool) –Whether the
controlsshould be built lazily/on-demand. -
cache_extent(Number | None) –Items that fall in the cache area (before or after the visible area that are about
-
clip_behavior(ClipBehavior) –How to clip the
controls -
controls(list[Control]) –A list of
Controls to display inside ListView. -
divider_thickness(Number) –If greater than
0thenDivideris used as a spacing between list view items. -
first_item_prototype(bool) –Whether the dimensions of the first item of
controls -
horizontal(bool) –Whether to layout the
controlshorizontally. -
item_extent(Number | None) –A fixed height or width (when
horizontalisTrue) -
padding(PaddingValue | None) –The amount of space by which to inset the children.
-
prototype_item(Control | None) –A control to be used as a "prototype" for all items,
-
reverse(bool) –Whether the scroll view scrolls in the reading direction.
-
semantic_child_count(int | None) –The number of children that will contribute semantic information.
-
spacing(Number) –The height of divider between the
controls.
Examples#
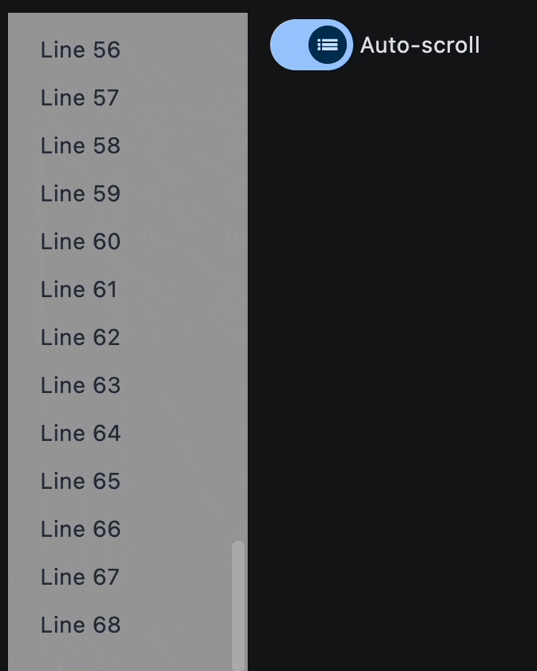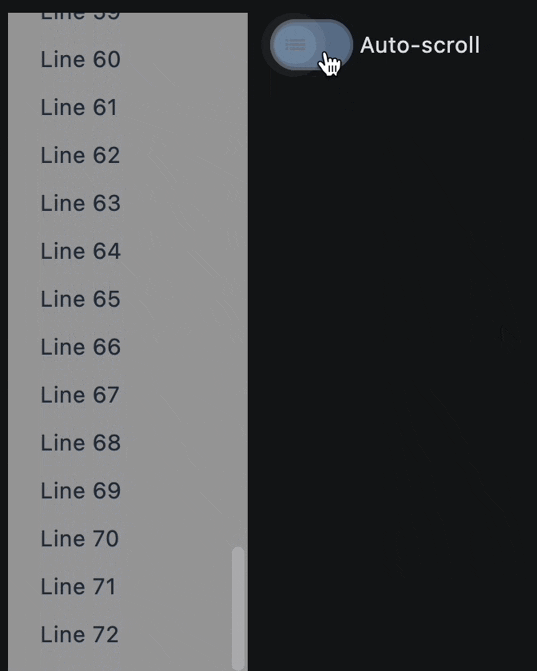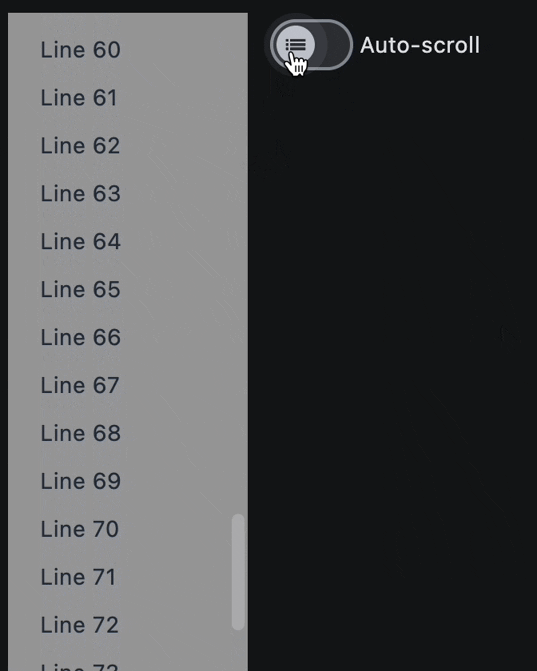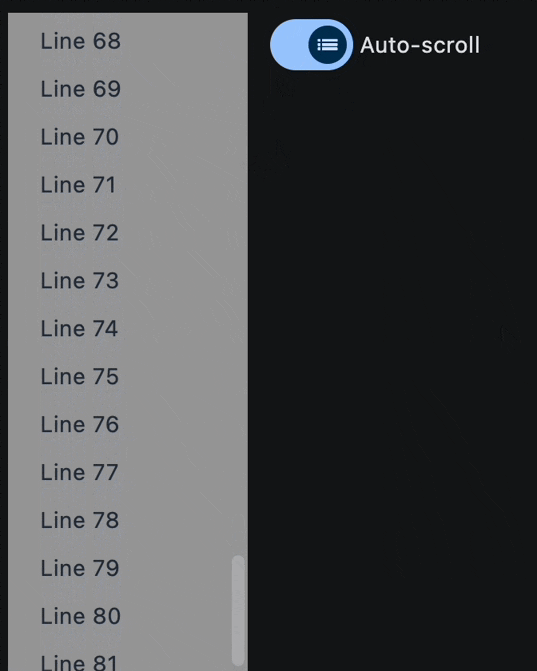
Auto-scrolling and dynamical items addition#
import asyncio
import flet as ft
async def main(page: ft.Page):
def handle_switch_change(e: ft.Event[ft.Switch]):
lv.auto_scroll = not lv.auto_scroll
page.update()
lv = ft.ListView(
spacing=10,
padding=20,
width=150,
auto_scroll=True,
controls=[
ft.Text(f"Line {i}", color=ft.Colors.ON_SECONDARY) for i in range(0, 60)
],
)
page.add(
ft.Row(
expand=True,
vertical_alignment=ft.CrossAxisAlignment.START,
controls=[
ft.Container(
content=lv,
bgcolor=ft.Colors.GREY_500,
),
ft.Switch(
thumb_icon=ft.Icons.LIST_OUTLINED,
value=True,
label="Auto-scroll",
label_position=ft.LabelPosition.RIGHT,
on_change=handle_switch_change,
),
],
)
)
# add a new item to the ListView every 1 second
for i in range(len(lv.controls), 120):
await asyncio.sleep(1)
lv.controls.append(ft.Text(f"Line {i}", color=ft.Colors.ON_SECONDARY))
page.update()
ft.run(main)
Properties#
build_controls_on_demand: bool = True
Whether the controls should be built lazily/on-demand.
This is particularly useful when dealing with a large number of controls.
cache_extent: Number | None = None
Items that fall in the cache area (before or after the visible area that are about to become visible when the user scrolls) are laid out even though they are not yet visible on screen.
The cache_extent describes how many pixels the cache area extends before the
leading edge and after the trailing edge of the viewport.
The total extent covered is:
cache_extent before + main axis extent + cache_extent after.
A list of Controls to display inside ListView.
divider_thickness: Number = 0
If greater than 0 then Divider is used as a spacing between list view items.
first_item_prototype: bool = False
Whether the dimensions of the first item of controls
should be used as a "prototype" for all other items,
i.e. their height or width will be the same as the first item.
item_extent: Number | None = None
A fixed height or width (when horizontal is True)
of an item to optimize rendering.
Note
This property has effect only when build_controls_on_demand
is True or spacing is 0.
prototype_item: Control | None = None
A control to be used as a "prototype" for all items,
i.e. their height or width will be the same as the prototype_item.
Note
This property has effect only when build_controls_on_demand
is True or spacing is 0.
reverse: bool = False
Whether the scroll view scrolls in the reading direction.
For example, if the reading direction is left-to-right and
horizontal is True,
then the scroll view scrolls from left to right when reverse is False
and from right to left when reverse is True.
Similarly, if horizontal is False, then the scroll view scrolls from top
to bottom when reverse is False and from bottom to top when reverse is True.